SSN#_____________________________________
You may not refer to any other materials during the exam. For each question (except otherwise explicitly stated), select the best answer for that question. Read all choices before selecting an answer and make sure your choice answers the question asked.
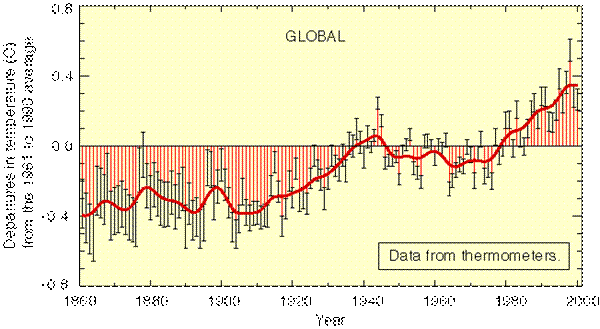
The above figure shows annual changes (anomalies) of the average global surface air temperature from 1861 to 2000 relative to 1961 to 1990 which is considered to be the baseline period. Please use this figure when answering Questions 1-5.
1. Which of the following statements is correct in describing the climate over the past 140 years:
a. mostly cold but with an overall warming trend
b. mostly warm but with an overall cooling trend
c. mostly warm but without any trend
d. mostly cold but without any trend
e. none of the above
2. Which of the following statements is correct in describing the climate over the past 25 years:
a. mostly cold but with a strong warming trend
b. mostly warm with a strong warming trend
c. mostly warm but without any trend
d. mostly cold but without any trend
e. none of the above
3. Which decades represent the warmest decades over the past 140 years?
a. 1960s
b. 1970s
c. 1980s
d. 1990s
4. Which year represents the warmest year over the past 140 years?
a. 1996
b. 1997
c. 1998
d. 1999
e. 2000
5. Which of the following is correct in describing the overall temperature trend over the past 140 years?
a. a warming by about 1.6°C
b. a warming by about 0.6°C
c. a cooling by about 0.6°C
d. a cooling by about 1.6°C
6. The climate of the last 1000 years can be characterized as:
a. a Medieval Warm Period, a cold Little Ice Age, and a warming trend since the late 19th century
b. a Younger-Dryas cold spell, a cold Little Ice Age, and a warming trend since the late 19th century
c. a mid-Holocene maximum, a Medieval Warm Period, and a cold Little Ice Age
d. a predominantly warm period
e. all of the above.
7. The climate of the last 1 million years can be characterized as:
a. mostly cold with relatively short warm periods
b. mostly cold but with a strong warming trend
c. mostly warm but with very strong glacial periods
d. mostly warm and dry
e. all of the above.
8. Which of the following is true about the oceans?
A. Approximately 3% of the total water on Earth is located in the oceans
B. The oceans cover about 30% of Earth’s surface
C. The average depth of the oceans is about 10 km.
D. The sea surface is level for all the oceans.
E. Because it takes far more energy to change the temperature of water than land or air, water warms up and cools off much more slowly than either.
9. The largest reservoir of water at the earth’s surface is
A. oceans
B. ice caps/glaciers
C. lakes/rivers
D. atmosphere
10. What is the primary salt in the ocean?
A. methane
B. CO2
C. FeO2
D. NaCl
11. The three primary forces that cause ocean surface currents are
A. Freezing, melting, and floating
B. El Nino, La Nina, and Southern Oscillation
C. Upwelling, downwelling, and sea floor spreading
D. Wind-induced frictional drag, Coriolis effect, and pressure gradients
E. Precipitation, evaporation, and runoff
12. Which of the following decrease salinity?
A. Evaporation
B. Precipitation
C. Melting of sea ice
D. River runoff.
E. All of the above except A.
13. Which of the following is true about the deep circulation of the oceans?
A. An overall "global conveyor belt" is formed that involves all the world’s oceans and that takes about 1,000 years for a complete cycle.
B. "North Atlantic Deep Water" is formed by very cold water from the Arctic zone and by salty water transported near the surface from the Equator.
C. The cold and salty water of the "North Atlantic Deep Water" is joined in the southern hemisphere by very cold water from Antarctica.
D. As the deep water currents from the Atlantic move northeastward through the Pacific they slowly rise to the surface because they are warmed up, and ultimately return to the Atlantic as surface currents.
E. All of the above.
For Questions 14-26, answer A for El Nino, B for La Nina, and C for both
B 14. A large-scale oceanic cooling of the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean
A 15. A large-scale oceanic warming of the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean
C 16. Influences weather and climate around the world
B 17. Easterly trade winds strengthen
A 18. Easterly trade winds weaken
B 19. Atmospheric pressure over Tahiti is higher than its normal high
A 20. Atmospheric pressure over Tahiti is lower than its normal high
B 21. The Southern Oscillation Index is strongly positive
A 22. The Southern Oscillation Index is strongly negative
A 23. The thermocline in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean is deeper than average
B 24. The thermocline in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean is shallower than average
C 25. Is part of ENSO process
C 26. A phenomenon in the Pacific Ocean
27. Which of the following is in the correct sequence from long to short term effects on climate?
A. deep ocean circulation – glacial and interglacial cycles – El Nino – seasonal changes in monsoon intensity
B. glacial and interglacial cycles – deep ocean circulation – El Nino – seasonal changes in monsoon intensity
C. glacial and interglacial cycles – El Nino – deep ocean circulation – seasonal changes in monsoon intensity
D. deep ocean circulation – glacial and interglacial cycles – seasonal changes in monsoon intensity – El Nino
E. none of the above
28. What would happen to sea level if all the ice caps melted?
A. it would rise by inches
B. it would fall by inches
C. it would rise by tens of meters
D. it would fall by tens of meters
E. it would not change
29. The present-day atmospheric CO2 concentration is most likely to be
A. 280 ppmv
B. 365 ppmv
C. 180 ppmv
D. 540 ppmv
E. 1000 ppmv
30. Ice cores and deep sea sediment cores show evidence that during the transition from the Last Glacial Maximum to the start of the Holocene period
A. periodic, massive melting events sent icebergs and freshwater to the North Atlantic Ocean
B. this massive inflow of freshwater reduced the salinity (and, hence, density) of the surface water to the point it stopped sinking
C. this inhibited the formation of North Atlantic deep water, thereby shutting down the ocean conveyor belt and rapidly creating a colder climate
D. all of the above
E. none of the above
31. During the Last Glacial Maximum,
A. the atmospheric CO2 concentration were higher than present
B. Gulf Stream flowed from Florida to Africa instead of Europe
C. tropical rainforests covered larger areas than today
D. the sea level were higher than present
E. all of the above
32. Which of the following statement is not true about the ice ages?
A. Ice age global circulation was globally windier as shown by the increased accumulation of dust in ocean sediments.
B. Earth’s climate tends to drift slowly into ice ages which are rapidly terminated by sudden warming.
C. Each time the Earth was locked in ice, the level of the oceans dropped from their present levels by 100-130 meters.
D. At the peak of ice ages, the forest-covered areas increased in size and the tundra biome was smaller in area.
33. By analyzing records taken from proxy sources, scientists can extend our understanding of climate far beyond the 140 year instrumental record. The proxy sources include
A. historical documents
B. tree rings and speleothems
C. corals and ice cores
D. ocean sediments
E. all of the above
34. The importance of understanding how climate has varied in the past lies in the fact that
A. past variability can show climatic extremes not experienced during recorded history
B. in order to understand the effects of human activity on climate, we must establish what the planet’s atmosphere and climate was like before human perturbations
C. constructing and interpreting long-term records of climate are the only means to determine how periodic climate change is
D. past is prologue
E. all of the above
For Questions 35-40 answer true (A) or false (B).
A 35. From a perspective of the Earth’s climate history, we are now living in a warm period, termed as interglacial.
A 36. A higher ratio of oxygen 18 to oxygen 16 in the ocean floor sediment record suggests a colder climate.
A 37. Melting of ice sheets can destabilize the circulation of the world’s oceans, and this can have a dramatic effect on climate.
B 38. During a major ice age, the ratio of oxygen 18 to oxygen 16 is higher in the ice caps than in the oceans.
A 39. Throughout much of the geologic past (before humanity arrived on the scene), the earth was much warmer than it is today.
B 40. During the El Nino years, the Texas’s winter climate tends to be drier and warmer than average.